Lower GI
1. Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Introduction
● Key Conditions: Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Crohn’s Disease (CD).
● Pathophysiology: Chronic inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract with relapsing and remitting courses.
● Epidemiology:
o Prevalence: Higher in Western countries, decreasing gradient from north to south, less common in Asia-Pacific.
o Peak incidence:
▪ UC: 15-30 years, smaller peak at 50-70 years.
▪ CD: 20–40 years, more common in Ashkenazi Jews.
o Genetic predisposition: Stronger in CD (e.g., NOD2 gene mutations).
o Risk Factors: Smoking cessation (UC), fast food, high sugar/meat, low fiber/fruit diets.
● Goals of Management: Tailored evidence-based interventions to achieve remission and prevent complications.
Ulcerative Colitis (UC)
Pathophysiology
● Immune dysregulation involving T-helper (Th2) cells.
● Overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-5, IL-13).
● Breakdown of epithelial barrier leading to continuous colonic inflammation.
● Histology: Goblet cell mucus depletion, crypt abscesses, crypt shortening/distortion.
Diagnosis
● Presentation: Bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, urgency, tenesmus.
● Endoscopic Findings:
o Continuous mucosal inflammation starting from the rectum.
o Loss of vascular pattern, friability, ulcers.
● Histology: Crypt distortion, basal plasmacytosis, diffuse inflammation.
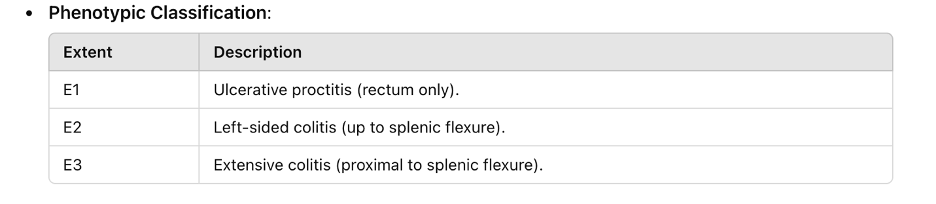
Treatment Targets
● Clinical Remission: Normal stool frequency, absence of rectal bleeding.
● Endoscopic Remission: Mayo score ≤2, mucosal healing (subscore ≤1).
● Histological Remission: Absence of inflammatory infiltrate.
Management of UC
Mild-to-Moderate Disease
- 5-ASA: Oral dose 2–4.8 g/day + enema for distal disease.
- Monitoring: U&E and renal function at baseline, 2–3 months, then annually.
- Side Effects: Nausea, diarrhea, paradoxical worsening of symptoms (3%).
- Steroids: Prednisolone 40–60 mg/day tapered over 8–12 weeks.
- Refractory Cases: Budesonide MMX (9 mg/day).
- Maintenance: Continue 5-ASA, add thiopurines if steroid-dependent.
Severe Disease
- Acute Severe UC (ASUC):
- Intravenous corticosteroids (hydrocortisone 100 mg QID).
- Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia.
- Avoid NSAIDs, opiates, and anticholinergics.
- Rescue Therapy:
- Infliximab: 5 mg/kg IV at weeks 0, 2, 6.
- Ciclosporin: 2 mg/kg/day IV.
- Surgical Options: Colectomy for refractory cases or toxic megacolon.
- 10-Year Colectomy Rates: Pancolitis 25%, left-sided colitis 8%.
Pouches and Pouchitis
● Definition: Inflammation of the ileal pouch following colectomy.
● Risk Factors: Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), retained rectal cuff.
● Management:
o Acute: Ciprofloxacin (500 mg BID for 2 weeks) or metronidazole.
o Chronic: Combination antibiotics, oral budesonide, probiotics for prophylaxis.
o Surveillance: Annual pouchoscopy for high-risk groups.
Crohn’s Disease (CD)
Pathophysiology
● Th1/Th17-mediated immune dysregulation.
● Overproduction of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-12, IL-23.
● Transmural inflammation causing strictures, fistulas, perforations.
● Histology: Granulomas, crypt distortion, lymphocytic aggregates.
Management of CD
Medications
- Steroids: Budesonide 9 mg/day for mild ileocolonic disease.
- Thiopurines: Azathioprine 2–2.5 mg/kg/day.
- Side Effects: Pancreatitis (0.1–2%), myelotoxicity, nausea.
- Monitoring: TPMT enzyme; thiopurine metabolites.
- Biologics:
- Anti-TNF: Infliximab, adalimumab.
- Anti-IL-12/23: Ustekinumab.
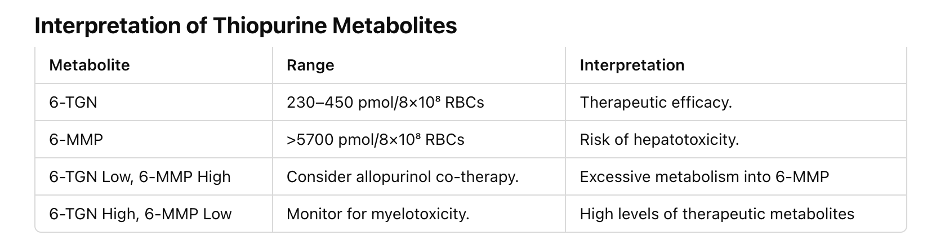
Rutgeerts Scoring
● i0: Normal mucosa, very low recurrence risk.
● i1: ≤5 aphthous ulcers, low recurrence risk.
● i2: Larger ulcers confined to the anastomosis, intermediate recurrence risk.
● i3: Diffuse aphthous ileitis, high recurrence risk.
● i4: Diffuse inflammation with larger ulcers, very high recurrence risk.
Surgical Management
● Strictureplasty or segmental resection for obstructive disease.
● Seton placement for perianal fistulas.
High-Yield Immunology Points
● Cytokines in UC: IL-5, IL-13 (Th2-mediated).
● Cytokines in CD: TNF-α, IL-6, IL-23, IL-17 (Th1/Th17-mediated).
● Therapeutic Targets:
o Anti-TNF (e.g., infliximab).
o Anti-integrin (e.g., vedolizumab).
o Anti-IL-12/23 (e.g., ustekinumab).
Extraintestinal Features
● Activity-Dependent:
o Erythema nodosum, aphthous ulcers, episcleritis.
● Independent of Activity:
o Pyoderma gangrenosum, uveitis, PSC, sacroiliitis.
● Management: Treat IBD; consider biologics for refractory conditions.
Pregnancy and IBD
● Safe Medications:
o 5-ASA, thiopurines, steroids, anti-TNF.
● Avoid: Methotrexate (teratogenic).
● Cautions:
o Ciclosporin linked to low birth weight.
Risk Factors for Relapse
● Non-adherence to therapy.
● Smoking (protective in UC, harmful in CD).
● CRP >5 mg/L, fecal calprotectin >300 µg/g.
● Male sex, prior steroid use.
References
- Lamb CA, Kennedy NA, Raine T, et al. "British Society of Gastroenterology consensus guidelines on the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults." Gut. 2019;68:s1–s106. Link.
- European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) Guidelines. Link.
- NICE Guidance for IBD. Link.